Introduction
Self-checkout systems have become a common feature in modern retail environments, revolutionizing the way consumers shop and pay for their purchases. Whether you’re at a grocery store, a pharmacy, or a department store, chances are you’ve encountered a self-checkout kiosk. These systems are designed to streamline the shopping experience, reduce wait times, and offer customers more control during checkout. But how exactly do they work, and what should businesses and consumers know about them? Everything you need to know about self-checkout systems is included in this comprehensive guide.
Definition
Self-checkout systems are automated point-of-sale (POS) solutions that allow customers to scan, bag, and pay for their purchases without the assistance of a cashier. Commonly found in retail stores and supermarkets, these systems aim to streamline the checkout process, reduce wait times, and enhance operational efficiency by enabling shoppers to complete transactions independently.
What Are Self-Checkout Systems?
Self-checkout systems are automated point-of-sale (POS) terminals that allow customers to scan, bag, and pay for their items without the assistance of a cashier. These systems typically include:
- Barcode scanners
- Touchscreen displays
- Payment modules (for cash, card, and digital wallets)
- Bagging areas with weight sensors
- Receipt printers
Some advanced setups also integrate with customer loyalty programs, mobile apps, and voice-guided assistance for accessibility.
How Do Self-Checkout Systems Work?
The basic workflow of a self-checkout system includes:
- Initiating the Transaction: The customer taps “Start” on the screen to begin.
- Scanning Items: Each item’s barcode is scanned using the built-in scanner. For produce or items without barcodes, customers can look them up on the touchscreen.
- Bagging: After scanning, items are placed in the bagging area, which has weight sensors to detect whether the correct item is being bagged.
- Payment: Once all items are scanned, the customer selects a payment method—credit/debit card, mobile payment, or sometimes cash.
- Receipt and Exit: After payment, a receipt is printed or emailed, and the transaction is complete.
Benefits of Self-Checkout Systems
Convenience for Shoppers:
Self-checkout kiosks reduce long lines and provide customers the flexibility to control their shopping experience. Many people prefer self-checkout, especially for quick or small purchases.
Operational Efficiency:
Retailers can reassign staff to other duties, such as restocking shelves or assisting customers on the floor, leading to better overall service without increasing labor costs.
Cost Savings:
While the initial setup cost is significant, self-checkout systems can lead to long-term savings by reducing the need for cashier staffing, particularly during off-peak hours.
Enhanced Throughput:
Self-checkout kiosks increase the number of available checkout points, which can improve store throughput and reduce customer wait times.
Challenges and Limitations
Theft and Shrinkage:
One of the biggest concerns with self-checkout systems is shoplifting or accidental non-scanning of items. Although systems use weight sensors and sometimes security cameras, they are still vulnerable to losses.
Technical Glitches:
Payment problems, scanner faults, or system errors can irritate clients and interrupt the shopping experience. Software upgrades and routine maintenance are essential.
Customer Hesitation:
Not all customers are comfortable using self-checkout, particularly older adults or those unfamiliar with technology. Providing a user-friendly interface and on-site assistance can help bridge this gap.
Initial Investment:
Installing self-checkout systems involves considerable upfront costs—for hardware, software, and employee training.
Types of Self-Checkout Systems
Self-checkout systems come in various formats, tailored to different retail environments:
Fixed Kiosks:
These are the most common type and are typically found in supermarkets and large retail chains. They are stationary and include full hardware for scanning and payment.
Mobile Self-Checkout:
Some stores offer mobile apps that allow customers to scan items as they shop and pay through their smartphones. This method is gaining popularity due to its convenience and minimal hardware requirements.
Hybrid Checkouts:
These systems allow for both cashier-assisted and self-service checkout at the same station. This is useful during peak hours when flexibility is needed.
Best Practices for Retailers
To ensure the success of self-checkout systems, retailers should follow these best practices:
Monitor Activity:
Employ staff to oversee self-checkout areas and assist when needed. Monitoring also helps deter theft and ensure smooth operations.
Optimize Interface Design:
The user interface should be intuitive, fast, and easy to navigate. Clear instructions, multi-language support, and accessibility features are key.
Train Staff Thoroughly:
Even with automation, human oversight is essential. Staff should be trained to troubleshoot issues, assist customers, and manage exceptions like age-restricted items.
Maintain Equipment Regularly:
Routine checks and maintenance of hardware and software prevent downtimes and maintain a positive user experience.
The Future of Self-Checkout
As technology evolves, self-checkout systems are becoming smarter and more integrated. Here are some emerging trends:
AI and Computer Vision:
Some advanced systems are using computer vision to eliminate the need for barcode scanning altogether. Amazon’s “Just Walk Out” technology is a prime example, where sensors and cameras track what customers pick up and automatically charge them.
Biometric Payments:
Facial recognition and fingerprint scanning are being explored to facilitate secure and seamless payment processes.
Voice-Controlled Checkout:
Voice assistance is being integrated into self-checkout to enhance accessibility and ease of use, especially for visually impaired users.
Integration with Loyalty Programs:
More systems now allow customers to log in to their accounts, redeem rewards, and apply personalized discounts directly at the self-checkout kiosk.
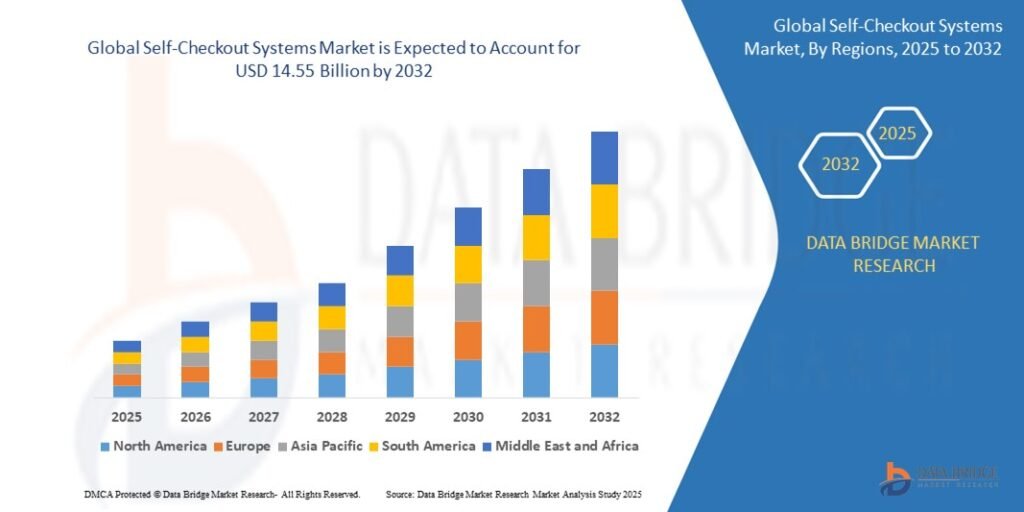
Growth Rate of Self-Checkout Systems Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the Self-Checkout Systems market is projected to grow from its 2024 valuation of USD 5.03 billion to USD 14.55 billion by 2032. The market is anticipated to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.20% between 2025 and 2032, mainly due to the growing need for automation in retail and labour cost reduction.
Conclusion
Self-checkout systems are transforming the retail landscape by offering convenience, reducing costs, and improving operational efficiency. While there are challenges to consider—such as theft, technical issues, and customer adoption—many of these can be addressed with thoughtful design and proper staff training. As innovation continues to push the boundaries of automation and artificial intelligence, the self-checkout experience is set to become even more seamless and personalized. For retailers, embracing this technology means staying competitive and meeting the evolving expectations of today’s tech-savvy consumers.